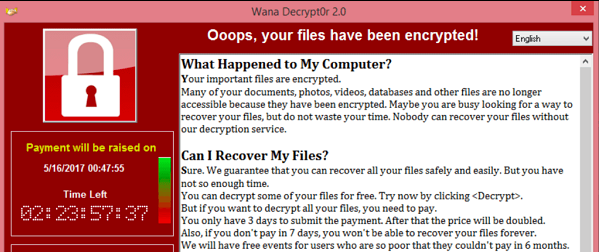
Governments, corporations and cybersecurity experts are still reeling after getting a taste of the most widespread ransomware attack to date. Only a few weekends ago, over 200,000 computers in 99 countries were hit by the unprecedented “Wanna” ransomware attack, also known as: WannaCry, WCry, WanaCrypt and WanaCrypt0r.
The British National Health Service was the first to report the attack, after several of its systems had been hit. Later, Spain’s largest telecommunications company Telefonica, and French carmakers Renault also admitted to being hit – among other government agencies, global organizations and corporations.
The WannaCry attack is a new one. But still one of the largest breaches in history, the 2014 JP Morgan Data Breach affected tens of millions of people, and seven million businesses—a total of 83 million customers. Five individuals used malware, social engineering, and spear-phishing attacks to plunder emails, addresses, phone numbers, SSNs, and other customer information, not just from JP Morgan itself, but other related financial institutions around the same time.
A Cyber Attack of Financial Market Data Could Paralyze the Markets
The swiftness in which the attack spread, and the fact that it easily infiltrated systems that are supposed to be responsible for our safety is particularly troubling: if hospitals and car manufacturers’ applications can get exploited so easily – financial data applications should not be any different, vulnerability wise.
The 2016 Financial Industry Cybersecurity Report summarized it all saying that Cybercrime has jumped to the second most reported economic crime in PWC’s Global Economic Crime Survey and financial institutions are prime targets. As cyber criminals find new ways to attack, breach, and exploit organizations, threat patterns such as phishing, spear-phishing, and social engineering evolve and become more sophisticated.
The 2016 Financial Industry Cybersecurity Report further lists the following findings:
- The U.S. Commercial bank with the lowest security posture is one of the top 10 largest financial service organizations in the U.S (by revenue);
- Only one of the top 10 largest banks, Bank of America, received an overall ‘A’ grade;
- 75% out of the top 20 U.S. commercial banks (by revenue) are infected with malware and several malware families were discovered within these banks, including Ponyloader, and Vertexnet.1
- 95% out of the top 20 U.S. commercial banks (by revenue) have a Network Security grade of “C” or below;
- Nearly 1 out of 5 financial institutions use an email service provider with severe security vulnerabilities.
The report authors summarize it all by saying that financial organizations need solutions that assess vulnerabilities and their vendor’s vulnerabilities in real-time.
Open source is everywhere. You can’t avoid it anymore. So, might as well manage it.
Understanding today’s application security challenges, one may want to acknowledge that software composition has changed fundamentally in recent years. A software program today typically consists of proprietary code, open source components and commercial libraries, while open source has become the most dominant part.
Forrester’s latest ‘software composition analysis’ report estimates that 60 to 80 percent of the average software product are open source components. Although open source has been central to increasing software developers’ productivity, it has also introduced new challenges into the software development process. The problem is most software development and security teams have not adapted well to handle these new challenges.
That’s why it’s important to make sure you:
- Keep track of all your software components: proprietary, third party and open source, so that you can locate vulnerabilities and mitigate them before the hackers get a chance to exploit your organization or product;
- Put an automated and continuous open source security management system in place to regularly track your components, alert your team about vulnerabilities and present the recommended fixes is a great step in the right direction;
- Define (and enforcing) a project lifecycle that embodies legal, security and quality standards common in regulated industries like financial services;
- Provide a project infrastructure that implements continuous automation across all hosted projects.
We’d love to hear your thoughts! How are you adapting to security challenges introduced by open source - and more importantly what processes have you introduced?
Patricia Johnson is an Open Source Security and Licensing Expert at WhiteSource.

